Understanding the Digestive and Excretory Systems
Table of Contents
A Simple Journey Through Your Body’s Processing Plants
The human body is a complex and miraculous machine, and at the heart of its operations are two essential systems that work tirelessly to keep us healthy: the digestive and excretory systems. These systems, often called the body’s processing plants, play crucial roles in breaking down the food we eat, absorbing essential nutrients, and eliminating waste. Let’s embark on a simple journey through these remarkable systems to grasp their functions and significance in maintaining our well-being.
The Digestive System: A Culinary Adventure
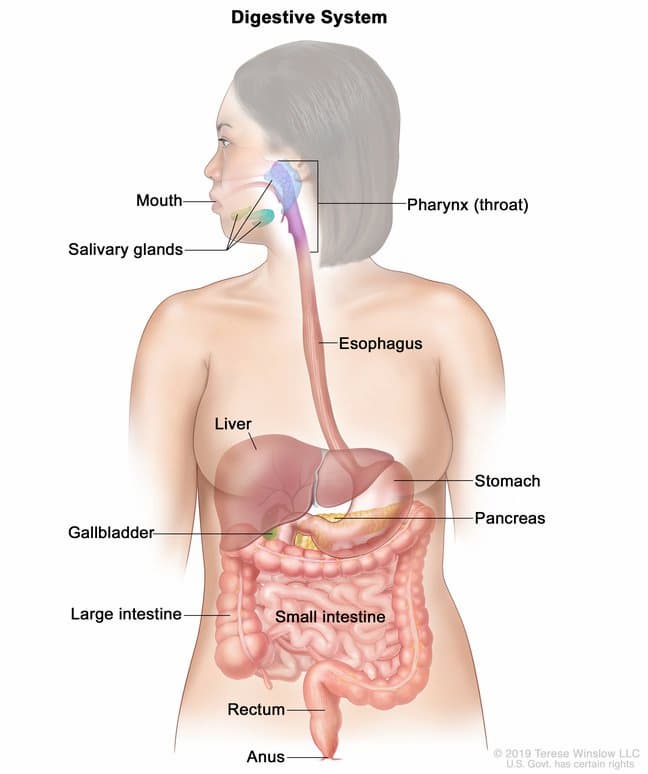
Imagine your digestive system as a well-organized kitchen where the process of turning food into energy begins. It all starts in your mouth, where digestion’s first step occurs. As you chew your food, the salivary glands release saliva, containing enzymes that begin breaking down carbohydrates.
Once thoroughly chewed, your food travels down the esophagus, a muscular tube, and enters the stomach. Here, the stomach acts as a mixing bowl, churning and breaking down the food into a semi-liquid substance called chyme. The stomach also secretes gastric juices that contain potent acids and enzymes to further break down proteins.
Next, the chyme moves into the small intestine, where the real magic happens. The small intestine is like a master chef’s workstation, equipped with enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver, which helps break down fats, proteins, and carbohydrates into smaller molecules. These tiny molecules are then absorbed through the intestinal walls into the bloodstream.
The journey doesn’t end there. The absorbed nutrients travel through the bloodstream to various body parts, providing energy and nourishment to cells, tissues, and organs. The remaining undigested material, now resembling a watery mixture, enters the large intestine.
In the large intestine, water is absorbed, and the indigestible remnants form feces. Like a waste disposal unit, the rectum stores the feces until it’s time for elimination. Finally, the anus acts as the exit door, allowing the body to get rid of waste in the form of solid stool.
The Excretory System: Filtering and Balancing
Now that we’ve explored the food journey through the digestive system let’s shift our focus to the excretory system, responsible for filtering and eliminating waste products from the body.
Picture the excretory system as a sophisticated filtration plant, with the kidneys taking center stage. The kidneys, shaped like beans, filter blood to remove waste and excess fluids, producing urine. This urine travels down tubes called ureters to reach the bladder, where it’s stored until you’re ready to release it.
The bladder, a muscular sac, expands as it fills with urine. When the bladder reaches capacity, a signal is sent to the brain, and you feel the urge to urinate. The urethra, a tube connected to the bladder, is the exit route for urine to leave the body.
Besides regulating fluid balance, the kidneys are crucial in maintaining the body’s electrolyte levels, such as sodium and potassium. These electrolytes are essential for various bodily functions, including nerve and muscle activity.
The digestive and excretory systems Importance of Balance
The digestive and excretory systems work harmoniously to maintain a delicate balance within the body. Imagine this balance as a seesaw – when one side goes up, the other comes down to maintain equilibrium.
Problems in one system can affect the other and disrupt this delicate balance. For instance, poor dietary habits may lead to digestive issues, impacting nutrient absorption and the kidneys’ ability to function correctly. On the flip side, kidney problems may lead to imbalances in fluid and electrolyte levels, influencing the digestive process.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity, supports these systems. Adequate hydration is essential to keep the digestive and excretory systems functioning smoothly.
Conclusion
In the grand scheme of our bodily functions, the digestive and excretory systems are unsung heroes, quietly working behind the scenes to keep us alive and well. Understanding these systems in simple terms allows us to appreciate the intricate processes within our bodies daily.
So, the next time you enjoy a meal or take a bathroom break, take a moment to thank your digestive and excretory systems for their incredible work. These unsung heroes keep you going, day in and day out.