Understanding Diabetic Complications
Written by: Marcos Otero, Retired Physician Associate
Diabetes, a condition that alters sugar processing in the body, can lead to several complications if not managed effectively. It is crucial to understand these common diabetic complications to grasp their impact and importance in preventing health risks.
1. Heart Disease and Stroke
People with diabetes are more likely to develop heart problems and strokes. High blood sugar can damage blood vessels, making it easier for fat deposits to build up. This can lead to blockages, increasing the risk of heart attacks or strokes.
Key Signs: Chest pain, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, or sudden weakness on one side of the body.
2. Kidney Damage (Diabetic Nephropathy)
High blood sugar, a result of diabetes, can harm the delicate blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to kidney disease or even failure over time. This underscores the importance of blood sugar control in preventing kidney damage.
Key Signs: Swelling in feet and ankles, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, or changes in urination.
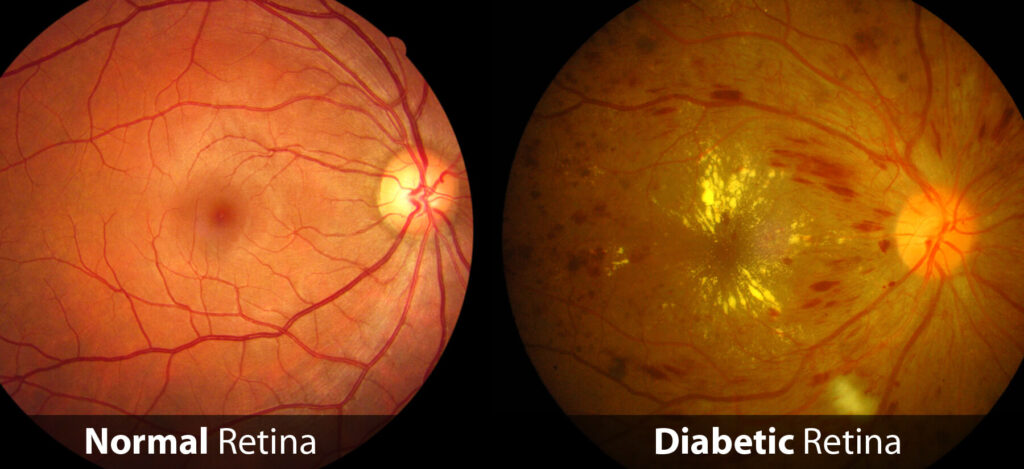
3. Eye Problems (Diabetic Retinopathy)
Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in your eyes, potentially leading to vision loss or blindness. Other conditions, like cataracts and glaucoma, are also more common in people with diabetes.
Key Signs: Blurred vision, dark spots, or difficulty seeing at night.
4. Nerve Damage (Diabetic Neuropathy)
High blood sugar can damage nerves throughout the body but often affects the feet and legs first. This can lead to pain, tingling, or numbness.
Key Signs: Burning or sharp pain, sensation loss, or coordination difficulty.
5. Foot Problems
Nerve damage and poor blood flow can lead to serious foot issues, like ulcers or infections. In severe cases, this might result in the need for amputation.
Key Signs: Open sores, infections, or loss of feeling in the feet.
6. Skin Infections and Conditions
People with diabetes are prone to skin problems, including bacterial or fungal infections. High blood sugar makes it easier for germs to grow.
Key Signs: Red, swollen, or itchy skin or persistent rashes.
7. Hearing Loss
Diabetes can damage the nerves and small blood vessels in the ears, leading to hearing difficulties.
Key Signs: Trouble following conversations or needing to increase volume levels.
8. Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia
Diabetes increases the risk of cognitive decline. Scientists believe that high blood sugar and insulin resistance may play a role in brain health.
Key Signs: Memory loss, confusion, or difficulty with problem-solving.
9. Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease)
High blood sugar can weaken the gums and bones that support teeth, making infections more likely and healing slower.
Key Signs: Red, swollen gums, bleeding when brushing, or loose teeth.
Prevention Tips
The good news is that managing your blood sugar can significantly reduce your risk of complications. Here are some tips:
- Monitor Your Blood Sugar: Check regularly and aim to keep it within the target range set by your doctor.
- Healthy Eating: Your diet plays a significant role in managing diabetes. By choosing foods that are low in sugar and high in fiber, such as vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, you can take control of your health and reduce your risk of complications.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise helps control blood sugar and keeps your heart healthy.
- Routine Checkups: Regular doctor, dentist, and eye specialist visits can catch problems early.
By staying informed and proactive, you can take charge of your health and live healthier, even with diabetes. Remember, taking small steps every day can make a big difference in avoiding complications.